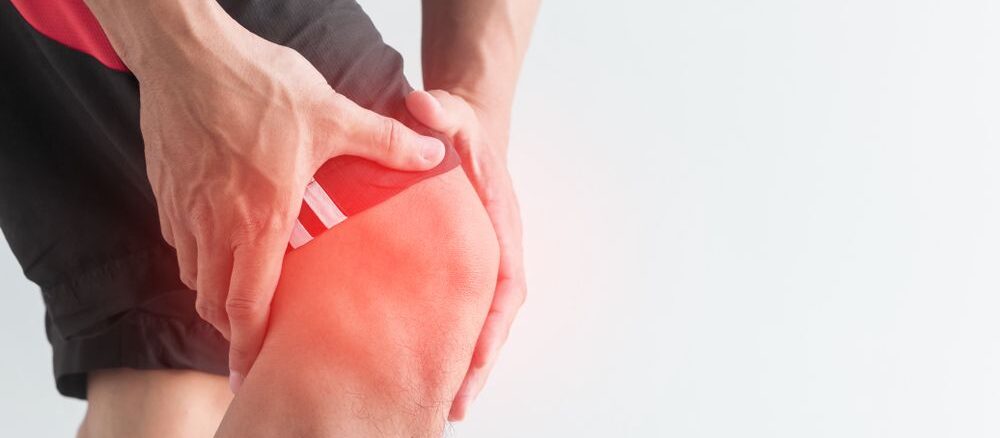
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that mainly affects the joints. The knee joint is one of the most commonly affected areas of Rheumatoid arthritis. It can cause pain, stiffness, and swelling, making it difficult for someone to carry out his routine activities. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for knee Rheumatoid arthritis.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Before delving into the specifics of knee rheumatoid arthritis, let’s first understand what rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is. RA is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues, leading to inflammation, pain, and joint damage. While RA can affect any joint in the body, the knees are often among the most commonly impacted
areas.
Symptoms of Knee Rheumatoid Arthritis
Pain and Stiffness
One of the earliest signs of knee RA is pain and stiffness in the knee joints, especially in the morning or after some time of inactivity. This discomfort can make it challenging to move the affected knee freely.
Swelling
The inflammation caused by RA can lead to noticeable swelling in the knee joints. Swollen knees can be painful and may even feel warm to the touch.
Reduced Range of Motion
Over time, knee RA can restrict the knee’s range of motion. This means that you may have difficulty bending or straightening your knee fully.
Warmth and Redness
Inflamed knee joints might feel warm to the touch and appear red due to increased blood flow to the affected area.
Fatigue
Rheumatoid arthritis often causes fatigue and overall tiredness, which can affect your ability to perform daily tasks.
Diagnosing Knee Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosing knee RA typically involves a combination of a thorough medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Here’s how the process usually works:
● Medical History: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and any family history of arthritis or autoimmune conditions. This information can help in determining the likelihood of RA.
● Physical Examination: Your doctor will carefully examine your knees, looking for signs of swelling, redness, warmth, and decreased range of motion. They may also check other joints to see if they are affected.
● Blood Tests: Blood tests are often used to detect specific antibodies that are associated with RA, such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies. High levels of these antibodies can be indicative of RA.
● Imaging Tests: X-rays and ultrasound may be performed to assess the extent of joint damage and inflammation in the knee.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, your doctor will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Treatment for Knee Rheumatoid Arthritis
The primary goals of treating knee RA are to manage pain, reduce inflammation, and prevent joint damage. Treatment plans often involve a combination of medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Here’s an overview of the common treatment options:
Medications
● Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These over-the-counter or prescription drugs can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
● Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs): These drugs, like methotrexate or sulfasalazine, are used to slow the progression of RA and protect the joints.
● Biologic Response Modifiers: Biologics, such as adalimumab or etanercept, target specific components of the immune system to reduce inflammation.
● Corticosteroids: Steroids can be injected into the knee joint to provide quick relief from pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapists can suggest exercises and techniques to improve knee strength, flexibility, and function. These exercises help maintain joint health and reduce pain.
Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in managing knee RA. Proper nutrition, regular exercise, and managing stress can help alleviate symptoms.
Assistive Devices
In some cases, the use of assistive devices like knee braces or orthopedic shoes can provide support and relieve pressure on the affected joints.
Surgery
In severe cases where conservative treatments are not effective, surgical options may be considered. These can include knee joint replacement surgery, where the damaged joint is replaced with an artificial one.
Living with Knee Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with knee RA can be challenging, but there are ways to improve your quality of life. Here are some tips for managing knee RA effectively:
Communicate with your healthcare team
Regularly discuss your symptoms and concerns with your healthcare providers, and be open to adjusting your treatment plan as needed.
Monitor your diet
A healthy, balanced diet can help manage RA symptoms and maintain overall health. Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and fatty fish, into your diet.
Maintain a healthy weight
Excess weight can put added stress on your knees. Losing weight, if necessary, can alleviate some of this stress and reduce pain.
Stay active
Regular low-impact exercise, such as swimming or gentle yoga, can help keep your knee joints flexible and strengthen the surrounding muscles.
Seek support
Joining a support group or speaking with a mental health professional can help you cope with the emotional and psychological aspects of living with RA.
Conclusion
Knee rheumatoid arthritis can be a challenging condition, but with early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan, it is possible to manage the symptoms and maintain a good quality of life. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider to discuss the best approach for your case. By understanding the symptoms, seeking a prompt diagnosis, and following a tailored treatment plan, you can take control of knee rheumatoid arthritis and
continue to enjoy a fulfilling and active life