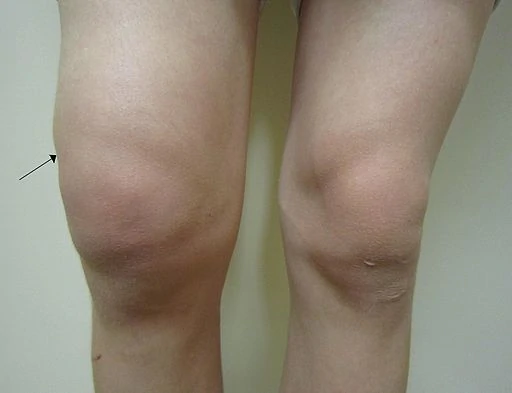
Knee injuries are very painful, and they can strike at any age. Knee swelling can reflect the body’s response to an injured knee. Knee swelling occurs when fluid accumulates in or around the knee joint. The pain comes first, followed by the worry over what just happened and then the swelling. Knee swelling and effusion that is mild to moderate can usually be treated at home. However, if the knee is continuously swollen or accompanied by significant pain or other serious symptoms, get medical help.
It’s critical to understand how to reduce swelling following a knee injury. In this blog, I will tell you the most effective method to heal the swelling of the knee at home. Therefore, read this blog to know the methods to manage a swollen knee at home, when to see a doctor, and how doctors use aspiration to remove fluid from a knee.
Best Approach To Treat a Swollen Knee at Home
You use the RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) approach to minimise swelling quickly and get back on your feet. Also, make an appointment with a medical specialist as soon as possible to find out what’s causing your pain and swelling!
Rest
Find a safe place to lie down and rest your knee as soon as possible after suffering a knee injury. If weight-bearing on the leg produces pain, wait until a medical practitioner has examined the knee to rule out a fracture or ligament tear before doing so again. Rest is essential for a thorough recovery and reduction of swelling to prevent additional damage.
Ice
After that, you should apply ice to the injured knee. Ice should be applied every hour or so in twenty-minute intervals. As ice restricts blood flow to the area, it is excellent for lowering swelling. To avoid skin harm from the very cold temperatures, wrap the ice pack in a towel. Ice is also excellent at reducing nerve activity in the treated area, thus it can help with pain relief after a knee injury.
Compression
Wrapping the knee with an ace bandage or any form of the elastic wrap can help relieve pain and minimise swelling. Wrap the knee securely, but not so tightly that circulation is cut off. It’s too tight if the area starts to feel numb, cold, or tingles. Compression is a fantastic method for safely lowering swelling and reducing pain.
Elevation
The final step in lowering swelling after an injury is to elevate the leg. It operates in the same way that the other techniques do, by reducing blood flow to the knee and therefore reducing swelling. Simply lie down on a couch or bed and rest your foot on some cushions. You can also lie on the floor with your legs against the wall vertically. To minimise knee swelling, your legs should be at least 45 degrees above your hips. This also makes you relax and relieve stress on your joints.
When to Contact a Doctor
The following are some symptoms that help people determine whether or not their knee swelling necessitates medical intervention.
A doctor should be contacted if:
- The knee is enlarged or has a noticeable deformity.
- The knee is unable to fully straighten or bend.
- The person is in unbearable pain
- The person is unable to bear weight on the knee.
- The skin on the knee becomes red or hot.
- The person has a temperature of 100.4° F or greater.
- Knee swelling has been present for more than three days.
A doctor will inspect the patient’s knee and ask various questions about it. The results of the physical examination and the patient interview may be sufficient to reach an accurate diagnosis. If more information is needed, the doctor may suggest medical imaging, such as an x-ray, or aspiration, an in-office technique that removes fluid from the knee.
Summary
I hope you have understood the method to reduce knee swelling after injury. The RICE approach is a good strategy to help alleviate inflammation and reduce swelling in many cases of knee injury. Anti-inflammatory drugs that are available over-the-counter can also be beneficial.
Consult a doctor if you’re concerned about swollen knees, have chronic knee discomfort, or are experiencing additional symptoms.